Exercising in the healing forest
The healing effects of this woodland health studio are supported by integrated health forests resting places and trails. A signposted network of trails of various degrees of difficulty help motivate visitors to movement. At various points in the forest, visitors are encouraged to participate in various physical and meditative exercises that promote holistic well-being. The curative and healing forest can be used both by patients from rehab clinics and by members of the general public to promote their own health and personal well-being.
Motor skills trail and meditative movement
The exercises are particularly recommended for diseases of the respiratory system, the skin, the musculoskeletal system, to strengthen the cardiovascular system and in patients with psychosomatic diseases.
We recommend that persons with limited mobility or restricted heart performance should be accompanied. Note the indicated degrees of difficulty.
Meditative movement therapy in the play of light and shadow
The beech (Fagus sylvatica) is the most common tree species in German forests. It provides shadow, humidifies the air and generally improves the climate.
Beech leaves contain many tannins, natural oils and iron and have germicidal and cooling properties. The leaves, like the sunflower, always turn towards the sun. The beech promotes health and strength, since it produces a lot of oxygen and keeps the forest air relatively free of dust.
Health maintenance, prevention and rehabilitation
Information boards show how to the use the exercise equipment properly with different variants as well as the training effects. The exercises serve to build muscle, help prevent falls, to train coordination, balance and concentration and to enhance perception.
Stations
- motorically active sitting
- balance beam
- balance board on springs
- one hundred steps
- tree trunk hopping course
- sensory perception path
- boulder obstacle course
- climbing circuit
- fourfold high bar
- meditative movement therapy
We present the stations below.
Advice
Warm-up: before exercises with, for example, shoulder and arm circles (forward/backward/opposite), diagonal stretching, forward bends, gentle stretching exercises.
End of exercise: gentle breathing and relaxation exercises, e.g. against trees.
Be careful in wet or icy conditions! Wear sturdy footwear.
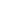
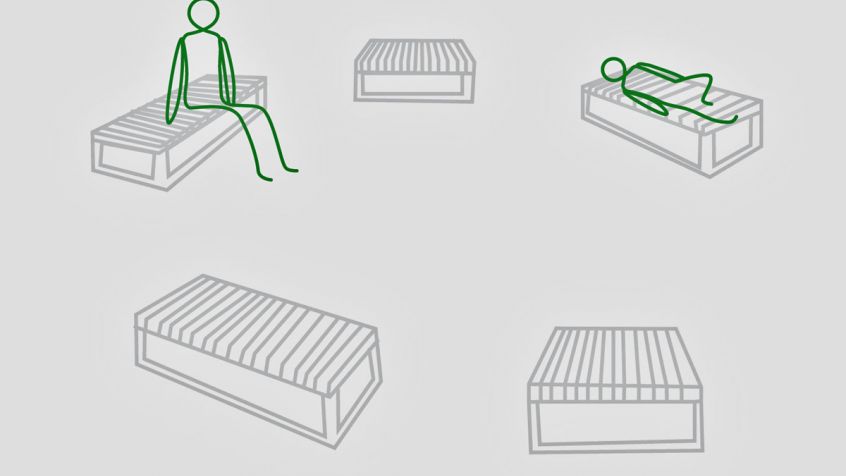
Motorically active sitting
Exercise: Sit carefully on the seat and find your balance. It’s not at all as easy as it sounds.
Training effect
- training of balance and coordination
- strengthening of the back and stomach musculature
- training of the pelvis musculature
Medical indication groups
Orthopaedic disorders
Psychosomatic illnesses
Difficulty
Easy
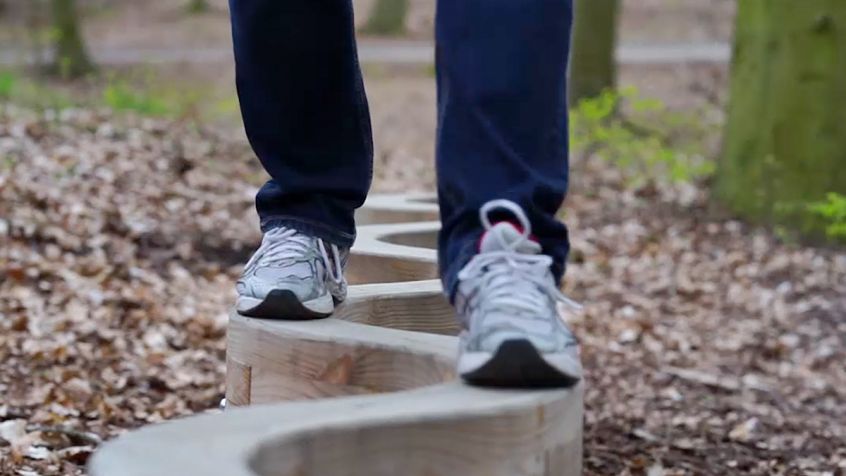
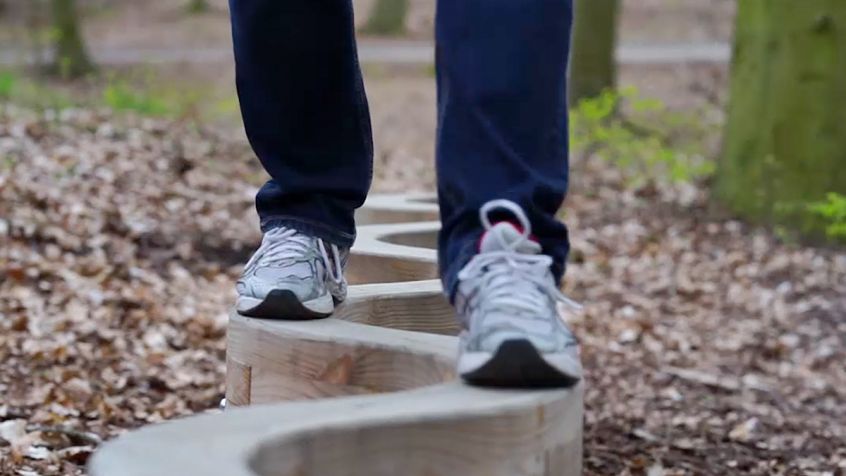
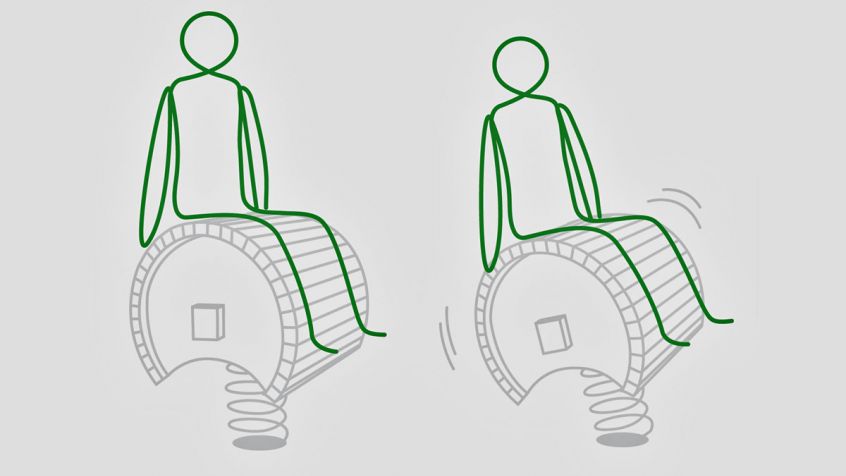
Curved balance beam
Exercise: Walk along the beam with alternating, precise setting down of the left and right foot. In a second Stage, you can also strength the left and right leg musculature by crouching.
Training effect
- improvement of balancing and control skills
- eye/leg coordination
- controlled movement sequences
- training of the general concentration
- improvement of body posture
Variants
- hold your arms against your hips and cover the course without the balancing effect of extended arms
- combine with coordinative tasks e.g. walk backwards or balance a book on your head
- partner exercises, e.g. hold hands and walk together as a "human snake" over the curved balancing beam
Medical indication groups
Orthopaedic disorders
Psychosomatic illnesses
Difficulty
Medium
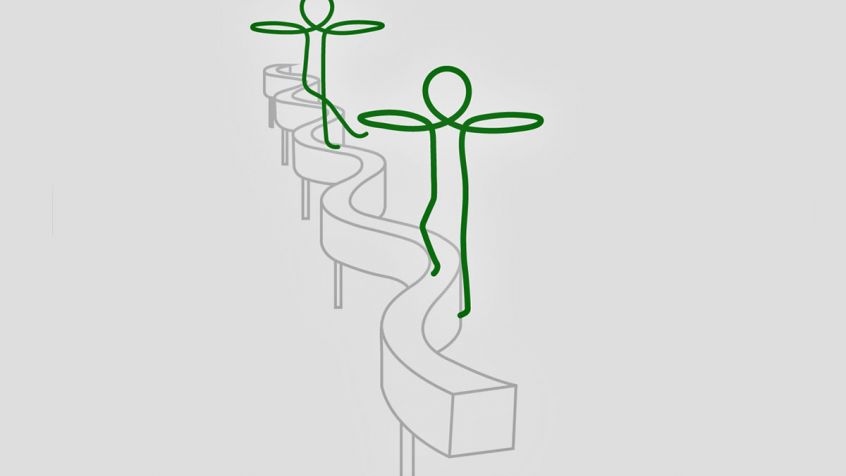
Balance board on springs
Exercise: Walking on the balancing board, alternating controlled setting down of the right and left foot. Maintaining balance by body tension and posture
Training effect
- improvement of balancing and control skills
- eye/leg coordination
- controlled movement sequences
- training of the arm and stomach musculature
- conscious adoption of optimum body posture
Variants
- hold your arms against your hips and cover the course without the balancing effect of extended arms
- combine with additional coordinative tasks e.g. Walk backwards or balance a book on your head
- partner exercises, e.g. hold hands and walk as a “human snake” over the balancing board
Medical indication groups
Orthopaedic disorders
Psychosomatic illnesses
Difficulty
Medium
One hundred footsteps
Exercise: This installation can only be used from one end. You cover the course by positioning the right and left feet in the appropriate shoe size (between 36-46) without touching the wooden surfaces. A foot position that is the reverse of the normal is desired.
Training effect
- training of balance and coordination
- breaking away from "entrenched movement patterns"
- prevention of falls
- harmonious interplay of muscles/muscle groups
Variants
- hold your arms against your hips and cover the course without the balancing effect of extended arms
- combine with coordinative tasks e.g. go backwards or balance a book on your head
Medical indication groups
Orthopaedic disorders
Psychosomatic illnesses
Difficulty
Easy
Tree trunk hopping course
Exercise: This installation can be used from both ends. Balance upright from trunk to trunk by alternately setting down your left and right foot in a controlled, precise way.
Training effect
- improvement of balancing and control skills
- breaking away from "entrenched movement patterns"
- coordination and strengthening of the stabilising musculature (especially the ankle and knee)
- check the pulse during training (heart function)
- recommendation: After each training unit, do loosening and relaxation exercises
Variants
- hold your arms against your hips and cover the course without the balancing effect of extended arms
- partner exercises, e.g. hold hands and walk together over the tree trunks
Medical indication groups
Respiratory tract disorders
Cardiovascular disease
Difficulty
Medium
Sensory perception trail with precision handrail
Exercise: Precision handrail: The wooden ring should be prevented from touching the curved handrail if possible! This task requires a very good spatial orientation and the highest degrees of concentration and precision.
Sensory perception: The course should be covered barefoot. Perception with the feet of the various trail surfaces. Also suitable for wheelchair users.
Training effects of precision handrail
- improved coordination
- eye/hand coordination
- strengthening of the trunk, shoulder and arm muscles
Training effects of sensory perception trail
- sensitisation of the soles of feet
- promotion of blood circulation in foot sole area
- promotion of arterial circulation
- strengthening of the trunk, shoulder and arm muscles
Variants for precision handrail
- racing against the clock or avoiding mistakes, with one or two rings
Variants for sensory perception trail
- combine with coordinative tasks e.g. walk backwards or balance a book on your head
- carefully walk with closed eyes over the different surfaces and guess what surface you can feel underfoot
- adjust pace, direction and route depending on difficulty
Medical indication groups
Orthopaedic disorders
Psychosomatic illnesses
Difficulty
Medium
Boulder obstacle course
Exercise: Negotiate the course from boulder to boulder as quickly and with as few errors as possible.
Training effect
- coordination/balance (controlled movement)
- improvement of balancing and control skills
- coordination and strengthening of the stabilising musculature (especially the ankle and knee)
- training for fall prevention
- training of the foot arch
Variants
- alternating controlled precise placement of the left and right foot on the boulders
- hold your arms against your hips and get across the boulders without the balancing effect of extended arms
- negotiate the course sideways
- partner exercises, e.g. hold hands and walk together over the boulders
- try to stand on one leg
- do the course barefoot
Medical indication groups
Orthopaedic disorders
Difficulty
Medium
Climbing circuit
Exercise: The installation can be used from both sides – climbing the individual sections or the entire route.
Training effect
- improvement of arm and leg coordination
- strengthening of the musculature of the upper and lower extremities
- improvement of sense of balance
- coordination training
Variants
- graduation by speed and precision
- personal benchmarking / group competition
- team training
Medical indication groups
Orthopaedic disorders
Cardiovascular disease
Difficulty
Difficult
Quadruple high bar
Exercise: This installation can be used from both sides – hanging and swinging exercises on the high bar.
Advice: Do warm-up exercises first (gentle hopping, easy stretching exercises).
Training effect
- improvement of the total body strength or body tone and the gymnastic skill
Variants
- jumping against the bar with locked arms
- hanging from the bar with bent arms and legs (5-15 secs)
- hanging from bar – knee to breast (5-15 secs)
- back swing out of locked arms position
- hip pullover
- back hip circle
- forward hip circle
- swinging when hanging from knees
Medical indication groups
Orthopaedic disorders
Cardiovascular disease
Difficulty
Difficult
Meditative movement therapy in the play of light and shadow
Exercise: Take the appropriate position (sitting, lying down), isometric exercises: Alternating tension/relaxation, breathing training and conscious perception of nature (play of light, tree movement, sounds)
Training effect
- training of perceptory functions
- relaxation until resting pulse is reached
Variants
- take the appropriate position (sitting, lying down)
- isometric exercises: alternating tension / relaxation
- breathing training
- conscious perception of nature (play of light, tree movement, sounds)
Medical indication groups
Respiratory tract disorders
Psychosomatic illnesses
Difficulty
Easy